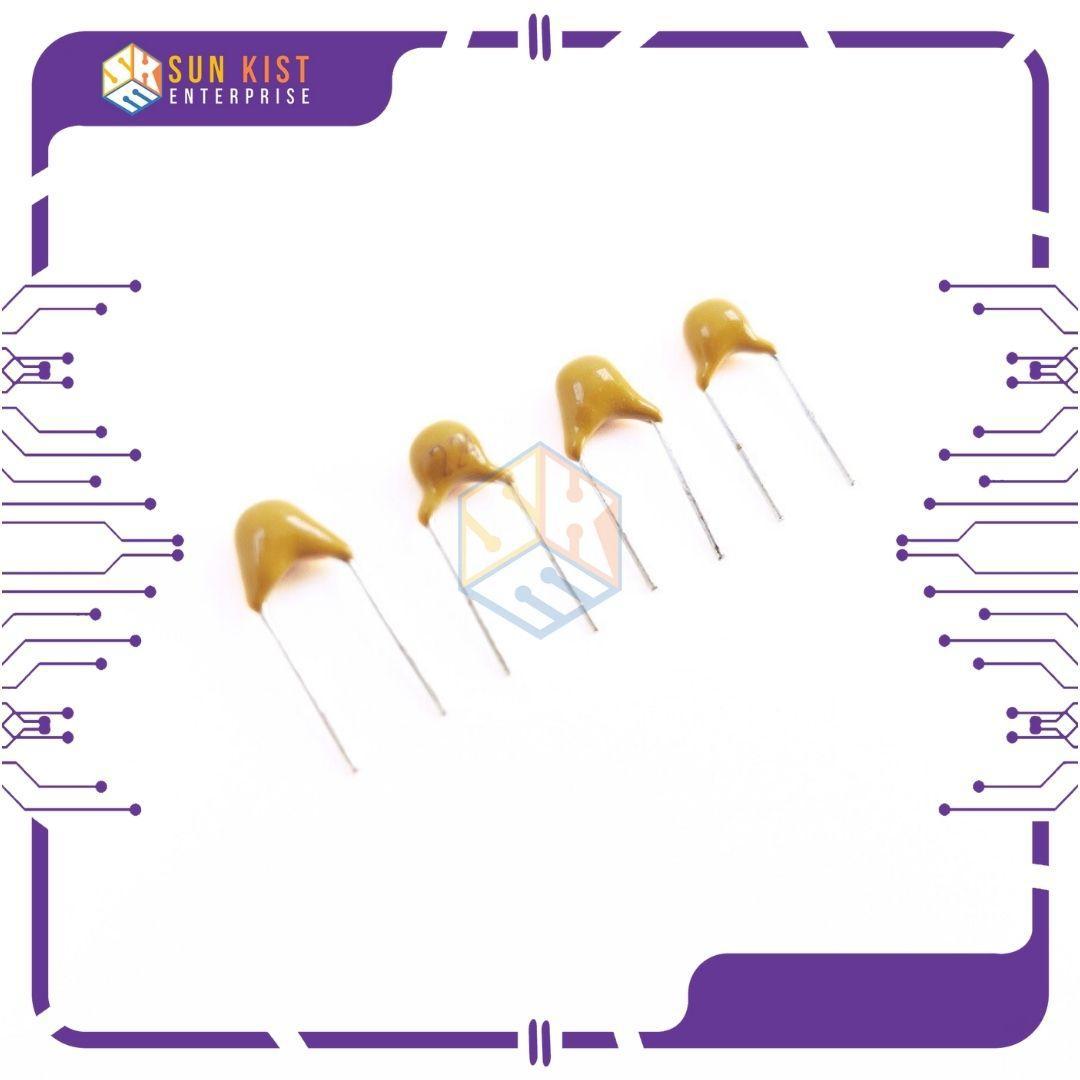
Description
A 220nF ceramic capacitor is a type of capacitor with a capacitance value of 220 nanofarads (nF). Here are some key details about a 220nF ceramic capacitor:
1. **Capacitance Value:**
– The capacitance value is 220 nanofarads, which is equivalent to 0.22 microfarads (µF).
2. **Dielectric Material:**
– Ceramic capacitors use a ceramic material as the dielectric. The type of ceramic material can affect the capacitor’s characteristics.
3. **Voltage Rating:**
– The voltage rating indicates the maximum voltage the capacitor can handle without breaking down. Common voltage ratings for ceramic capacitors range from a few volts to several hundred volts.
4. **Tolerance:**
– The tolerance specifies the allowed variation in the capacitance value from the nominal value. Common tolerances for ceramic capacitors include ±5%, ±10%, and ±20%.
5. **Temperature Coefficient:**
– The temperature coefficient indicates how much the capacitance value changes with temperature. Common temperature coefficients for ceramic capacitors include C0G (NP0), X7R, and Y5V.
6. **Package Type:**
– Ceramic capacitors are available in various package types, including radial leaded (through-hole) and surface mount (SMD) configurations. The package type determines how the capacitor is mounted on a circuit board.
7. **Applications:**
– Ceramic capacitors, including those with a capacitance of 220nF, are used in a wide range of electronic circuits. They are suitable for filtering, decoupling, coupling, and other applications.
8. **High-Frequency Characteristics:**
– Ceramic capacitors are known for their good high-frequency characteristics, making them suitable for applications in RF (radio frequency) and digital circuits.
9. **Non-Polarity:**
– Ceramic capacitors are non-polarized, meaning they can be connected in either direction in a circuit.
10. **Availability:**
– 220nF ceramic capacitors are readily available and are standard components used in many electronic designs.
When selecting a capacitor for a specific application, it’s important to consider the voltage requirements, tolerance, temperature stability, and other parameters that match the circuit’s needs. The actual part number or series of the capacitor may provide more detailed specifications, so it’s advisable to refer to the datasheet or product documentation for precise information.