Description
The 7809 is a popular linear voltage regulator integrated circuit (IC) that belongs to the 78xx series. Specifically, the 7809 is designed to provide a regulated output voltage of +9 volts. Here’s a brief description of the 7809 voltage regulator:
Type: Linear Voltage Regulator – The 7809 is a linear voltage regulator, which means it regulates the output voltage by dissipating excess energy as heat. Linear regulators are known for their simplicity and low-noise operation.
Output Voltage: +9 volts – The primary function of the 7809 is to provide a stable and regulated +9V DC output voltage, regardless of changes in the input voltage or load conditions.
Input Voltage Range: The input voltage range for the 7809 is typically a few volts above the desired output voltage. For stable operation, the input voltage should be higher than 9 volts but not exceed the maximum specified input voltage.
Regulation: The 7809 has built-in voltage regulation, ensuring a relatively constant output voltage despite changes in input voltage or load. The regulation is typically within a specified tolerance range, and it helps provide a stable power supply for connected circuits.
Current Handling Capacity: The 7809 is available in different variants with varying current-handling capacities. Common variants include the 7809 with a 1A (ampere) current rating.
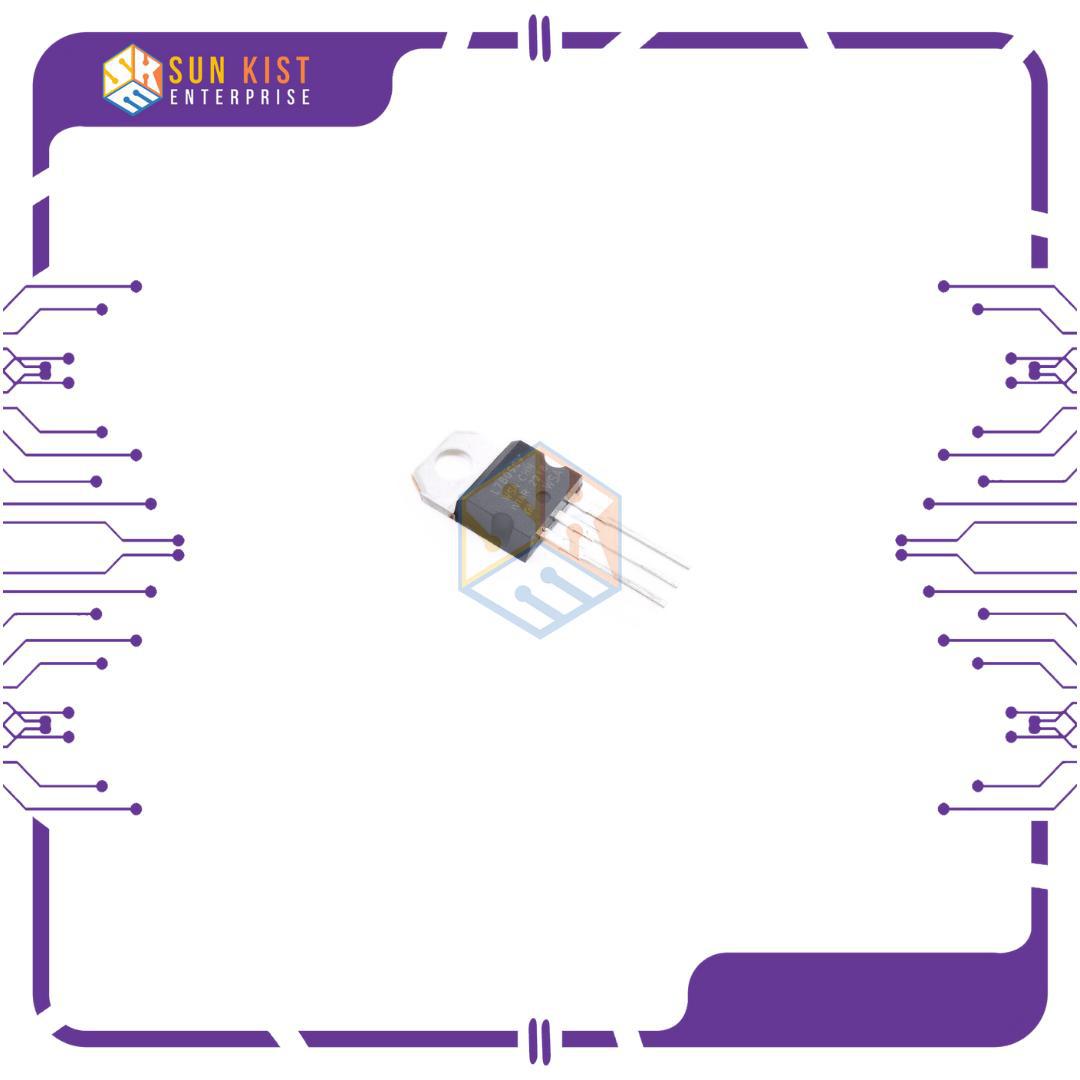
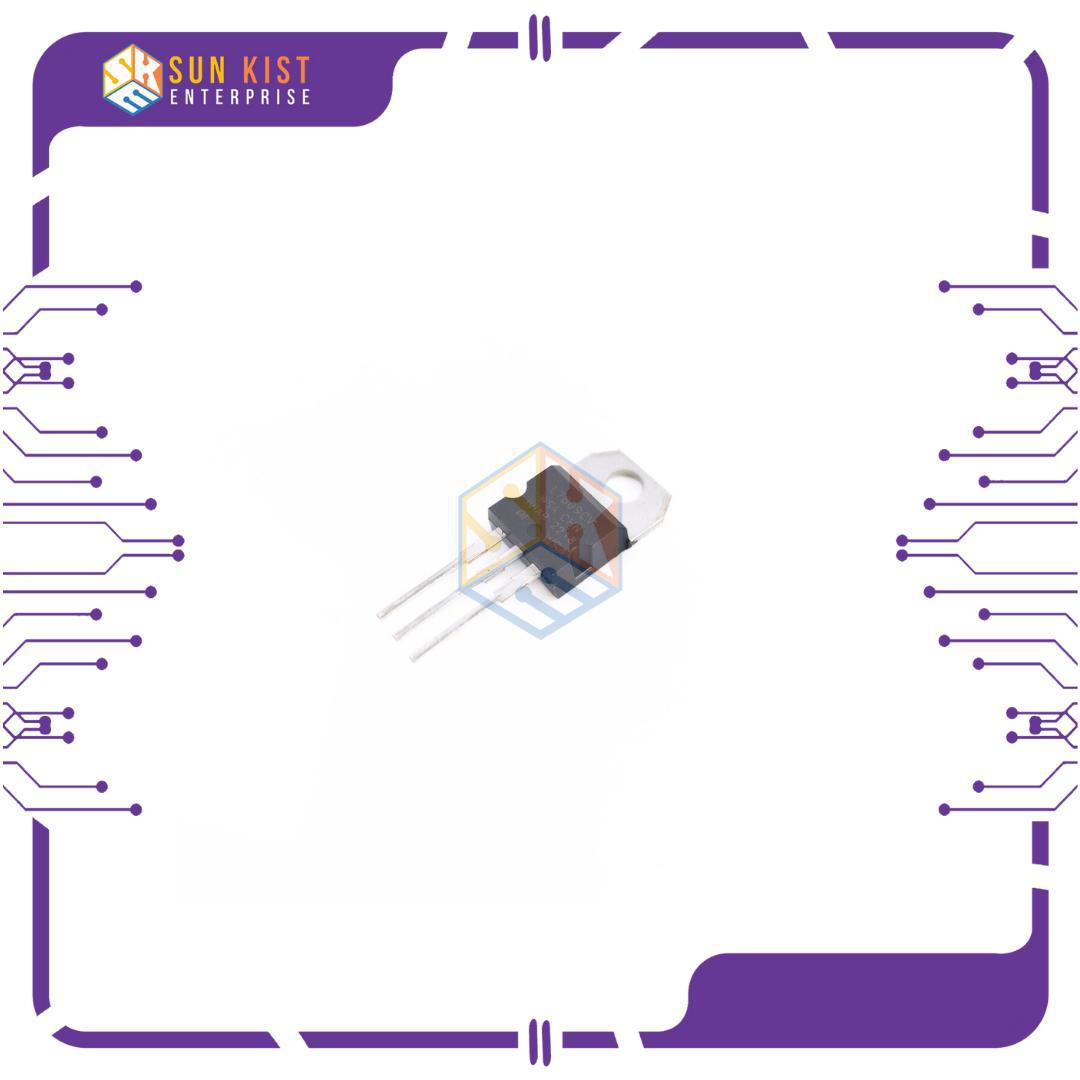
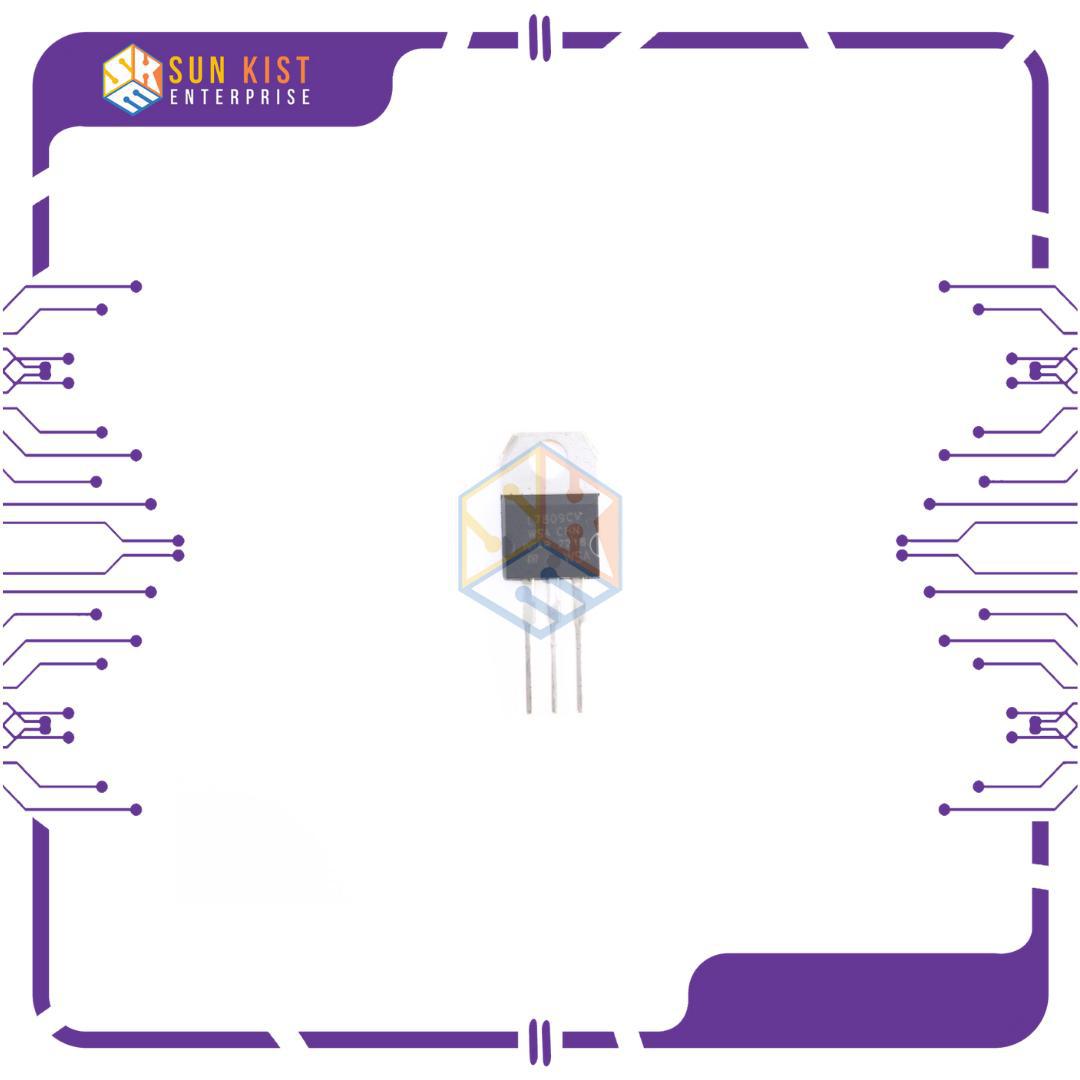
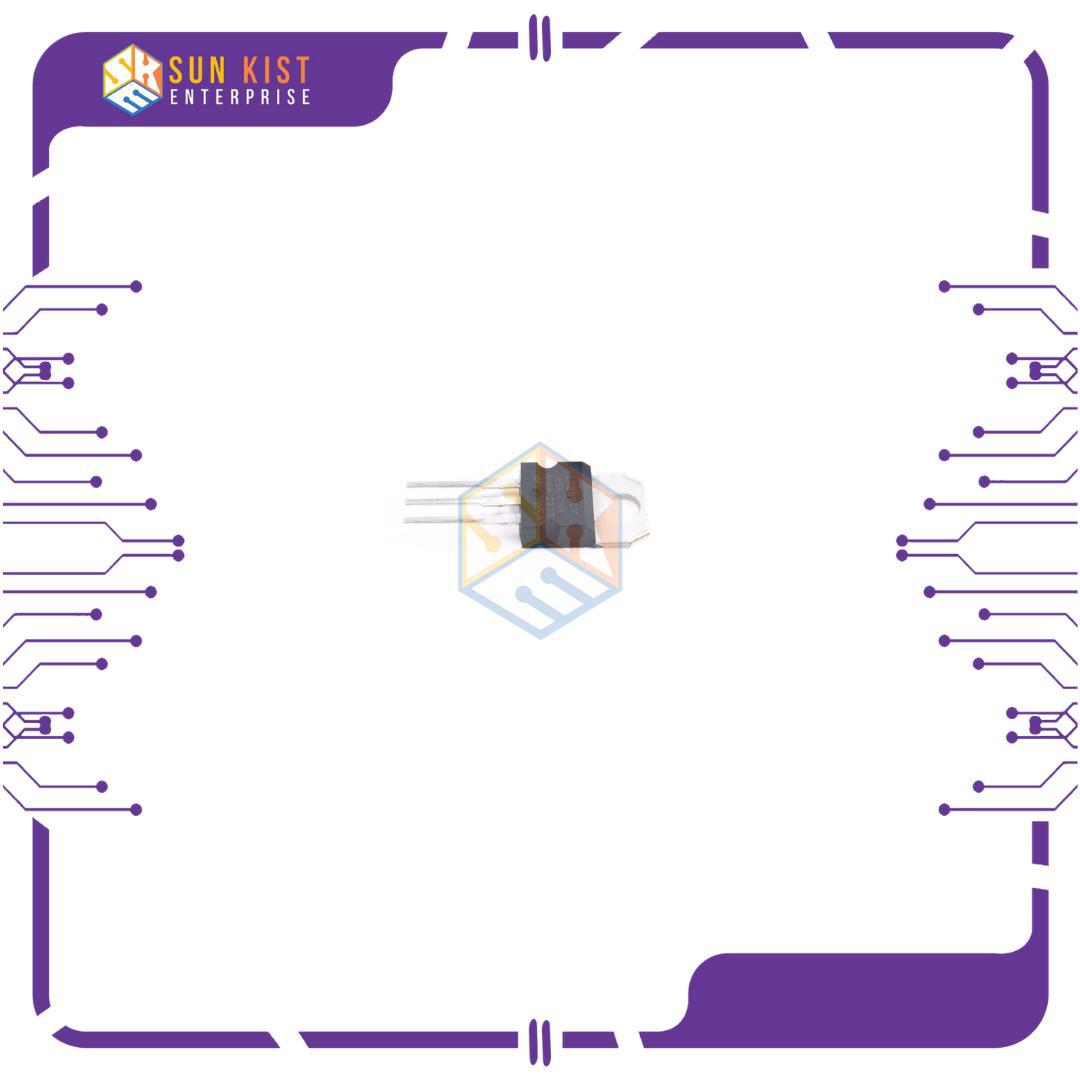
Package: The 7809 is available in various packages, such as TO-220 and TO-92, which are popular through-hole packages for easy mounting on a printed circuit board.
Pin Configuration: The 7809 usually has three pins:
Pin 1: Input (Vin)
Pin 2: Ground (GND)
Pin 3: Output (+9V)
Applications: The 7809 is commonly used in electronic circuits where a stable and regulated +9V power supply is required, such as in analog and digital circuits, microcontroller projects, and other electronic devices.
When using the 7809 or any voltage regulator, it’s important to follow the manufacturer’s datasheet for proper circuit connections, input voltage considerations, and heat dissipation requirements. Additionally, be aware of the power dissipation and use appropriate heatsinking if necessary, especially when dealing with higher input-output voltage differentials or higher currents.